2 min
The science behind the blood moon: Understanding this lunar phenomenon ahead of march's event
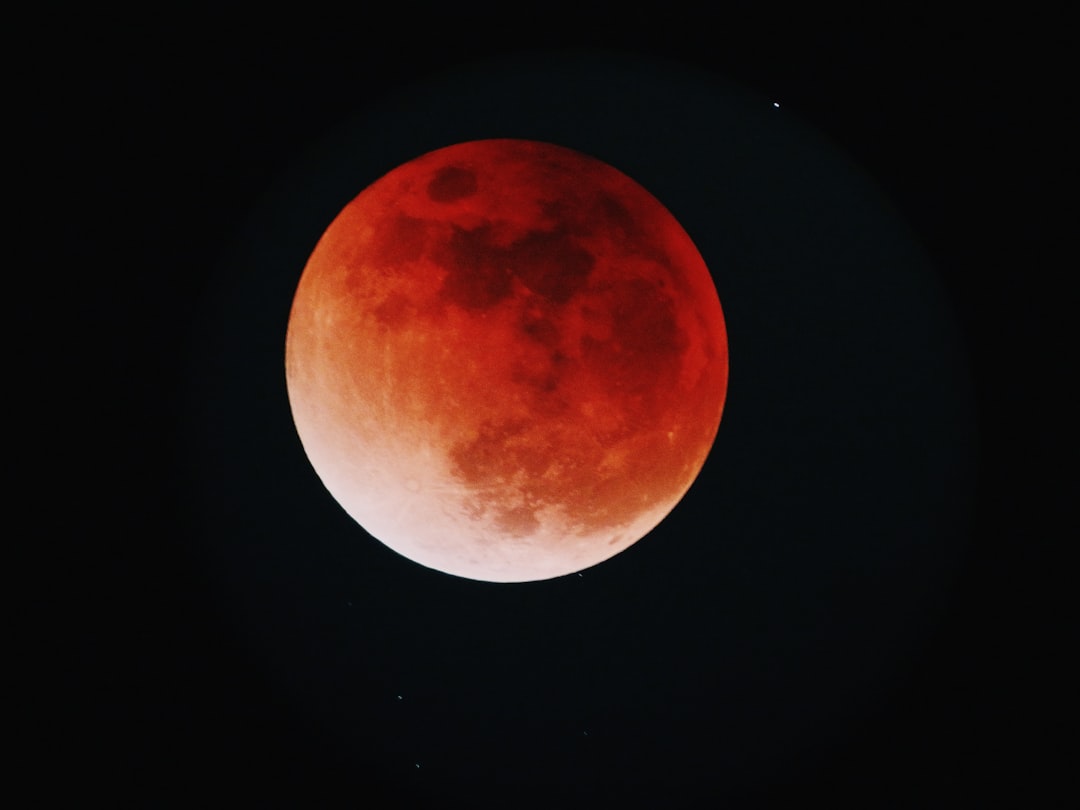
March's celestial event – a blood moon – is just around the corner. This captivating lunar spectacle isn't just a cool sight to behold; it has some neat science backing it up. The blood moon phenomenon happens during a total lunar eclipse. "During a total lunar eclipse, the only light that reaches the surface of the moon is refracted through the Earth's atmosphere, which essentially acts like a lens. Light is a wave, and every color of the rainbow has a different wavelength – red the longest and violet the shortest," said Bennett Maruca, associate professor of physics and astronomy at the University of Delaware. What adds to the excitement is the rare nature of total lunar eclipses. While partial eclipses occur more frequently, a full blood moon isn't an everyday event. Depending on where you live, the blood moon may only grace the night skies a few times a decade. "One of my favorite things about total lunar eclipses is that it's hard to know ahead of time quite what it will look like. The moon can take on a color ranging from burnt orange to red to grayish brown," he said. "The closer the Moon passes to the center of Earth's shadow, the darker the color will be." Maruca is available to speak about the event, which takes place in the wee hours of March 3. He can discuss when to wake up to see the phenomenon and how to best capture it. "For photographing the moon, I would recommend a camera with some optical zoom – the moon is only about 0.5 degrees across. Because of the low lighting conditions, a tripod or other support would be helpful since a longer exposure time will be needed," he noted. He has appeared in a number of outlets including Mashable and The Philadelphia Inquirer. He can be contacted by clicking on his profile. ABOUT BENNET MARUCA Bennett Maruca serves as an associate professor in the University of Delaware's department of physics and astronomy. His research focuses on the sun, the solar wind and other space plasmas. He is a recipient of the Antarctic Service Medal and NASA's Silver Achievement Medal. He also serves as an associate director of the Delaware Space Grant Consortium and is currently mentoring over twenty undergraduate students developing experiments to fly into space to observe Earth's ionosphere.