2 min
Oil Shock: How the War in Iran Could Send Global Fuel Prices Soaring
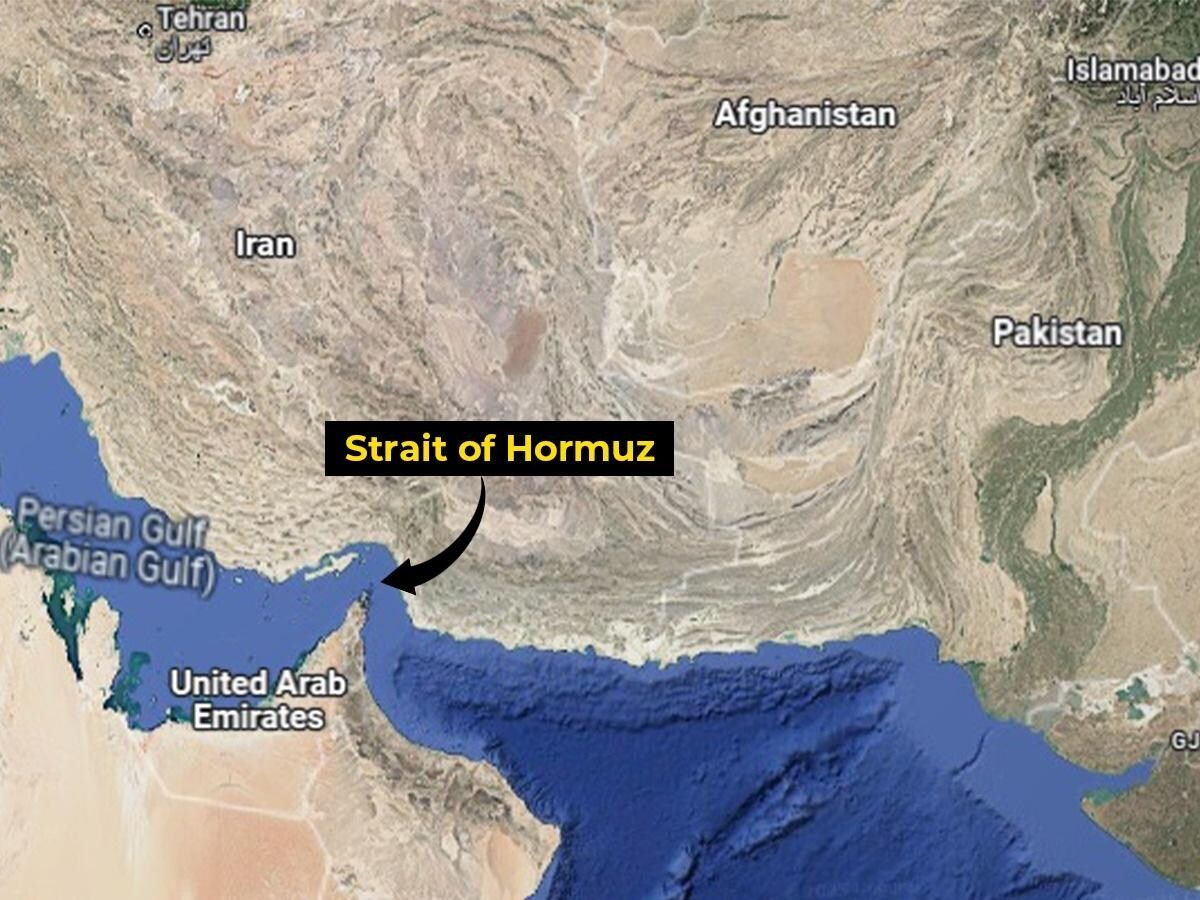
The ongoing war involving Iran has rapidly become one of the most consequential energy stories in the world. Oil markets have reacted sharply as military escalation threatens critical energy infrastructure and shipping routes in the Persian Gulf. Brent crude prices have surged past $100 per barrel as traders react to supply disruptions and the growing risk that the conflict could persist or expand across the region. At the heart of the concern is the Strait of Hormuz, a narrow but vital shipping corridor through which roughly one-fifth of the world’s oil and liquefied natural gas flows. Any disruption to this route has immediate ripple effects across global energy markets, transportation costs, supply chains, and ultimately consumer fuel prices. Analysts warn that if disruptions continue, the world could face sustained higher oil prices, tighter energy supply, and inflationary pressure across multiple sectors including transportation, manufacturing, and food production. In some scenarios, oil prices could climb significantly higher if shipping through the region remains restricted or if energy infrastructure becomes a sustained target in the conflict. For journalists covering the evolving situation, the energy implications of this conflict are complex and rapidly changing. From geopolitical strategy and energy security to economic ripple effects and consumer fuel prices, reporters need credible expert voices who can explain what’s happening and what comes next. ExpertFile connects journalists with leading experts across energy economics, geopolitics, global supply chains, and international security who can provide timely analysis on questions such as: Why the Strait of Hormuz is so critical to global oil markets How war in the Middle East impacts gasoline and diesel prices worldwide Whether oil prices could spike to $120 or higher The economic ripple effects of energy shocks on inflation and global markets How governments and energy companies respond to supply disruptions What the conflict could mean for long-term energy security and global trade Journalists covering the global energy story can connect with the many experts available through ExpertFile to provide context, analysis, and insight as this rapidly evolving crisis unfolds. Our experts can help! Connect with more experts here: www.expertfile.com