You might also like...
Check out some other posts from ExpertFile
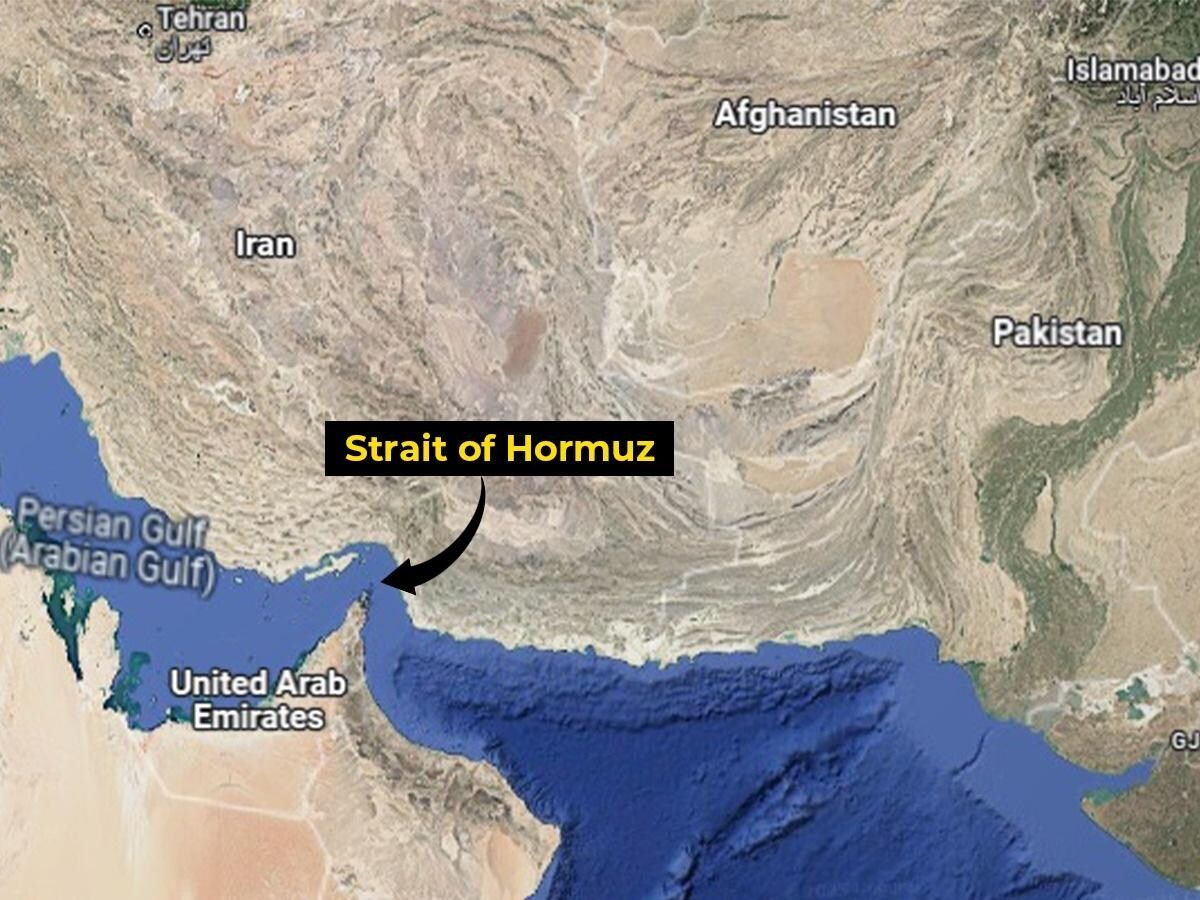
The Strait of Hormuz is one of the most strategically vital waterways on Earth. Just 20 miles wide at its narrowest point, with shipping lanes only a few miles across in each direction, this narrow channel connects the Persian Gulf to the Gulf of Oman and the Arabian Sea. Through it flows roughly one-fifth of the world’s petroleum supply, along with vast quantities of liquefied natural gas, particularly from Qatar.
For global markets, the Strait is more than geography, it is a pressure point. Any disruption, even the threat of one, can send oil prices surging and rattle financial markets worldwide.
A History Shaped by Empire and Energy For centuries, the Strait served as a maritime corridor linking Mesopotamia, Persia, India, and East Africa. Control over it shifted between regional powers, colonial empires, and eventually modern nation-states.
In the 16th century, the Portuguese seized nearby islands to dominate regional trade routes. Later, British naval power asserted influence during the height of imperial shipping dominance. In the 20th century, however, the Strait’s importance expanded dramatically with the rise of oil exports from Gulf states.
After the 1979 Iranian Revolution, tensions surrounding the Strait intensified. During the Iran-Iraq War in the 1980s, particularly the so-called “Tanker War” phase, commercial vessels were targeted, highlighting how vulnerable global energy supplies could be. Since then, periodic confrontations between Iran, the United States, and regional powers have kept the Strait at the centre of geopolitical risk.
Why It Is So Important Today 1. Energy Security Major oil producers including Saudi Arabia, Iraq, the UAE, Kuwait, and Qatar rely heavily on this route. Even short-term closures could disrupt millions of barrels per day in global supply.
2. Global Economic Stability Because oil is globally traded and priced, disruptions in the Strait impact fuel costs, inflation, shipping, and consumer prices worldwide — including in North America and Europe.
3. Military Strategy The Strait is bordered primarily by Iran to the north and Oman to the south. Iran has periodically threatened to close the passage in response to sanctions or military pressure. The U.S. Navy and allied forces maintain a consistent presence to ensure freedom of navigation.
4. Modern Geopolitical Flashpoint Recent decades have seen drone seizures, tanker detentions, and naval standoffs. Each incident reinforces how fragile global energy logistics can be when concentrated in a single corridor.
The Strait as a Symbol of Interdependence The Strait of Hormuz underscores a central truth of globalization: the world’s economies are deeply interconnected and geographically vulnerable. A narrow stretch of water in the Middle East can influence gasoline prices in Ontario, manufacturing costs in Germany, and energy security debates in Asia.
It is both a trade artery and a geopolitical lever — a reminder that geography still shapes global power.
Expert Angles for Media An expert in geopolitics, energy economics, or maritime security could explore: How vulnerable is the global economy to a prolonged closure? Can alternative pipelines realistically replace Hormuz traffic? What role do regional alliances play in deterring conflict? How does the Strait shape Iran’s negotiating power? What would insurance and shipping markets do in a crisis? The Strait of Hormuz is not simply a map feature — it is one of the world’s most consequential strategic chokepoints. Its stability underpins global energy flows, economic predictability, and international security.
If tensions rise there, the world feels it.
Our experts can help! Connect with more experts here: www.expertfile.com

Few figures bridge the worlds of street-level activism and presidential politics like Jesse Jackson. For more than six decades, he has stood at the center of America’s ongoing struggle for racial justice, economic fairness, and political inclusion.
His legacy isn’t just historical, it continues to shape today’s debates about voting rights, coalition politics, economic equity, and the power of grassroots organizing.
From Civil Rights Foot Soldier to National Leader Jesse Jackson rose to national prominence as a close associate of Martin Luther King Jr., working with the Southern Christian Leadership Conference during the height of the Civil Rights Movement.
He was present in Memphis in 1968 during King’s assassination, a moment that profoundly shaped his path forward. After King’s death, Jackson focused on translating civil rights gains into economic opportunity, founding Operation PUSH (People United to Save Humanity), later merging it into the Rainbow PUSH Coalition.
His central message: political rights mean little without economic power. The 1984 & 1988 Presidential Campaigns In 1984 and again in 1988, Jackson ran for the Democratic presidential nomination — becoming one of the first Black Americans to mount a serious, nationwide campaign for the presidency.
His 1988 campaign was especially historic:
He won 11 primaries and caucuses. He finished second in the Democratic race. He built what he called a “Rainbow Coalition” — uniting Black voters, Latinos, labor groups, farmers, progressives, and working-class Americans. Jackson expanded voter registration efforts and brought millions of new voters into the political process, laying groundwork for future candidates, including Barack Obama.
Coalition Politics Before It Was a Buzzword Long before diversity became corporate language, Jackson was preaching multiracial, multi-class political alliances. His philosophy emphasized:
Economic justice alongside civil rights Voting access and political representation Corporate accountability International human rights engagement He also engaged in diplomatic efforts abroad, including negotiating the release of American hostages in conflict zones — demonstrating how civil rights leaders could operate on the global stage.
Controversies and Complexity Jackson’s career was not without controversy. Critics pointed to past inflammatory remarks and political missteps. Yet even his detractors acknowledge his role in permanently expanding the boundaries of American politics.
He forced national conversations about race, poverty, and representation — and shifted the Democratic Party’s platform toward broader inclusion.
A Legacy That Endures Today’s conversations about:
Structural inequality Voter suppression Grassroots political mobilization Multiracial coalition building … all carry echoes of Jackson’s work.
Whether viewed as a trailblazer, a bridge between eras, or a polarizing figure, Jesse Jackson helped redefine what political participation looks like in America.
Connected with an expert Find more experts here: www.expertfile.com

Valentine’s Day may now be synonymous with chocolates, flowers, and heart-shaped everything, but its origins are far more complex, blending ancient Roman traditions, Christian martyrdom, and medieval storytelling.
What began as a mid-winter festival tied to fertility and renewal eventually evolved into a celebration of romantic love - one shaped as much by poets and pop culture as by saints and religious history.
Ancient Roots: Before Romance, There Was Ritual Long before Valentine’s cards, ancient Romans celebrated Lupercalia, a mid-February festival focused on fertility, purification, and the coming of spring. The event included symbolic rituals meant to ward off evil spirits and promote health and fertility, far removed from today’s candlelit dinners.
As Christianity spread through the Roman Empire, many pagan festivals were re-interpreted or replaced with Christian observances, laying the groundwork for what would become Valentine’s Day.
Who Was Valentine, Anyway? There isn’t just one Valentine. Historical records point to multiple early Christian martyrs named Valentine, the most famous being Saint Valentine, executed in the 3rd century CE.
One popular legend claims he secretly performed marriages for young couples despite a Roman ban, acts that ultimately led to his execution. While historians debate the accuracy of these stories, they helped cement Valentine’s association with love, sacrifice, and devotion.
Love Enters the Story: Medieval Poets Change Everything Valentine’s Day as a romantic holiday didn’t truly take shape until the Middle Ages. English poet Geoffrey Chaucer is often credited with linking February 14 to romantic love in his poetry, helping popularize the idea that it was the day birds chose their mates.
From there, the connection between Valentine’s Day and courtly love spread across Europe, especially among the nobility, eventually giving rise to handwritten love notes and tokens of affection.
From Handwritten Notes to Hallmark By the 18th and 19th centuries, Valentine’s Day had become a popular occasion for exchanging cards, flowers, and gifts. The Industrial Revolution made printed cards widely available, transforming a once-elite tradition into a mass-market celebration.
Today, Valentine’s Day is a global cultural phenomenon, equal parts romance, commerce, and tradition, evolving to include friendships, self-love, and inclusive expressions of connection.
It isn’t just about romance, it reflects how traditions evolve over time, absorbing layers of culture, religion, and storytelling. Understanding its history helps explain how societies redefine love, relationships, and celebration across generations.
Our experts can help! Connect with more experts here: www.expertfile.com





