2 min
Jesse Jackson: The Activist Who Turned Protest into Political Power
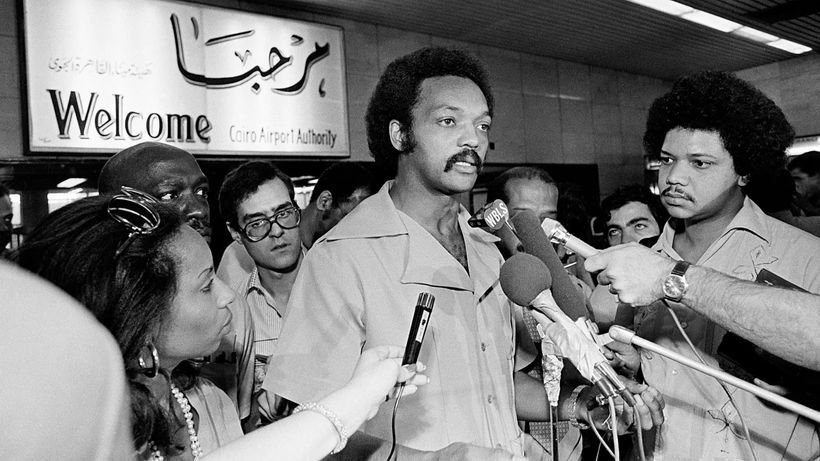
Few figures bridge the worlds of street-level activism and presidential politics like Jesse Jackson. For more than six decades, he has stood at the center of America’s ongoing struggle for racial justice, economic fairness, and political inclusion. His legacy isn’t just historical, it continues to shape today’s debates about voting rights, coalition politics, economic equity, and the power of grassroots organizing. From Civil Rights Foot Soldier to National Leader Jesse Jackson rose to national prominence as a close associate of Martin Luther King Jr., working with the Southern Christian Leadership Conference during the height of the Civil Rights Movement. He was present in Memphis in 1968 during King’s assassination, a moment that profoundly shaped his path forward. After King’s death, Jackson focused on translating civil rights gains into economic opportunity, founding Operation PUSH (People United to Save Humanity), later merging it into the Rainbow PUSH Coalition. His central message: political rights mean little without economic power. The 1984 & 1988 Presidential Campaigns In 1984 and again in 1988, Jackson ran for the Democratic presidential nomination — becoming one of the first Black Americans to mount a serious, nationwide campaign for the presidency. His 1988 campaign was especially historic: He won 11 primaries and caucuses. He finished second in the Democratic race. He built what he called a “Rainbow Coalition” — uniting Black voters, Latinos, labor groups, farmers, progressives, and working-class Americans. Jackson expanded voter registration efforts and brought millions of new voters into the political process, laying groundwork for future candidates, including Barack Obama. Coalition Politics Before It Was a Buzzword Long before diversity became corporate language, Jackson was preaching multiracial, multi-class political alliances. His philosophy emphasized: Economic justice alongside civil rights Voting access and political representation Corporate accountability International human rights engagement He also engaged in diplomatic efforts abroad, including negotiating the release of American hostages in conflict zones — demonstrating how civil rights leaders could operate on the global stage. Controversies and Complexity Jackson’s career was not without controversy. Critics pointed to past inflammatory remarks and political missteps. Yet even his detractors acknowledge his role in permanently expanding the boundaries of American politics. He forced national conversations about race, poverty, and representation — and shifted the Democratic Party’s platform toward broader inclusion. A Legacy That Endures Today’s conversations about: Structural inequality Voter suppression Grassroots political mobilization Multiracial coalition building … all carry echoes of Jackson’s work. Whether viewed as a trailblazer, a bridge between eras, or a polarizing figure, Jesse Jackson helped redefine what political participation looks like in America. Connected with an expert Find more experts here: www.expertfile.com