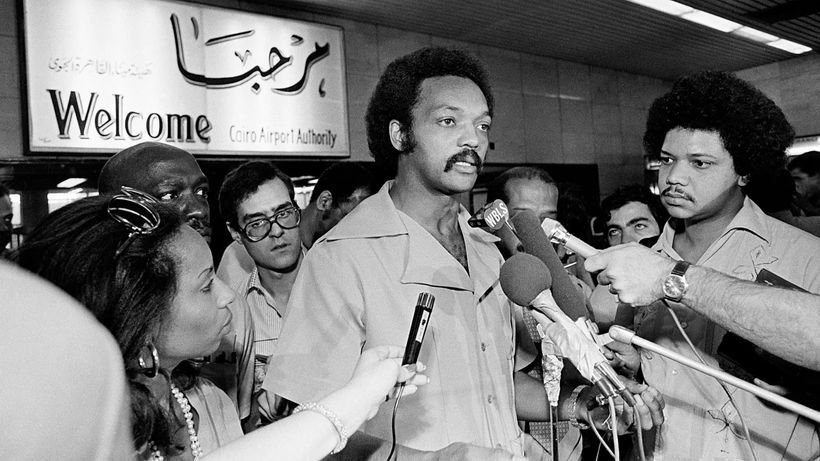
Few figures bridge the worlds of street-level activism and presidential politics like Jesse Jackson. For more than six decades, he has stood at the center of America’s ongoing struggle for racial justice, economic fairness, and political inclusion.
His legacy isn’t just historical, it continues to shape today’s debates about voting rights, coalition politics, economic equity, and the power of grassroots organizing.
From Civil Rights Foot Soldier to National Leader Jesse Jackson rose to national prominence as a close associate of Martin Luther King Jr., working with the Southern Christian Leadership Conference during the height of the Civil Rights Movement.
He was present in Memphis in 1968 during King’s assassination, a moment that profoundly shaped his path forward. After King’s death, Jackson focused on translating civil rights gains into economic opportunity, founding Operation PUSH (People United to Save Humanity), later merging it into the Rainbow PUSH Coalition.
His central message: political rights mean little without economic power. The 1984 & 1988 Presidential Campaigns In 1984 and again in 1988, Jackson ran for the Democratic presidential nomination — becoming one of the first Black Americans to mount a serious, nationwide campaign for the presidency.
His 1988 campaign was especially historic:
He won 11 primaries and caucuses. He finished second in the Democratic race. He built what he called a “Rainbow Coalition” — uniting Black voters, Latinos, labor groups, farmers, progressives, and working-class Americans. Jackson expanded voter registration efforts and brought millions of new voters into the political process, laying groundwork for future candidates, including Barack Obama.
Coalition Politics Before It Was a Buzzword Long before diversity became corporate language, Jackson was preaching multiracial, multi-class political alliances. His philosophy emphasized:
Economic justice alongside civil rights Voting access and political representation Corporate accountability International human rights engagement He also engaged in diplomatic efforts abroad, including negotiating the release of American hostages in conflict zones — demonstrating how civil rights leaders could operate on the global stage.
Controversies and Complexity Jackson’s career was not without controversy. Critics pointed to past inflammatory remarks and political missteps. Yet even his detractors acknowledge his role in permanently expanding the boundaries of American politics.
He forced national conversations about race, poverty, and representation — and shifted the Democratic Party’s platform toward broader inclusion.
A Legacy That Endures Today’s conversations about:
Structural inequality Voter suppression Grassroots political mobilization Multiracial coalition building … all carry echoes of Jackson’s work.
Whether viewed as a trailblazer, a bridge between eras, or a polarizing figure, Jesse Jackson helped redefine what political participation looks like in America.
Connected with an expert Find more experts here: www.expertfile.com

Valentine’s Day may now be synonymous with chocolates, flowers, and heart-shaped everything, but its origins are far more complex, blending ancient Roman traditions, Christian martyrdom, and medieval storytelling.
What began as a mid-winter festival tied to fertility and renewal eventually evolved into a celebration of romantic love - one shaped as much by poets and pop culture as by saints and religious history.
Ancient Roots: Before Romance, There Was Ritual Long before Valentine’s cards, ancient Romans celebrated Lupercalia, a mid-February festival focused on fertility, purification, and the coming of spring. The event included symbolic rituals meant to ward off evil spirits and promote health and fertility, far removed from today’s candlelit dinners.
As Christianity spread through the Roman Empire, many pagan festivals were re-interpreted or replaced with Christian observances, laying the groundwork for what would become Valentine’s Day.
Who Was Valentine, Anyway? There isn’t just one Valentine. Historical records point to multiple early Christian martyrs named Valentine, the most famous being Saint Valentine, executed in the 3rd century CE.
One popular legend claims he secretly performed marriages for young couples despite a Roman ban, acts that ultimately led to his execution. While historians debate the accuracy of these stories, they helped cement Valentine’s association with love, sacrifice, and devotion.
Love Enters the Story: Medieval Poets Change Everything Valentine’s Day as a romantic holiday didn’t truly take shape until the Middle Ages. English poet Geoffrey Chaucer is often credited with linking February 14 to romantic love in his poetry, helping popularize the idea that it was the day birds chose their mates.
From there, the connection between Valentine’s Day and courtly love spread across Europe, especially among the nobility, eventually giving rise to handwritten love notes and tokens of affection.
From Handwritten Notes to Hallmark By the 18th and 19th centuries, Valentine’s Day had become a popular occasion for exchanging cards, flowers, and gifts. The Industrial Revolution made printed cards widely available, transforming a once-elite tradition into a mass-market celebration.
Today, Valentine’s Day is a global cultural phenomenon, equal parts romance, commerce, and tradition, evolving to include friendships, self-love, and inclusive expressions of connection.
It isn’t just about romance, it reflects how traditions evolve over time, absorbing layers of culture, religion, and storytelling. Understanding its history helps explain how societies redefine love, relationships, and celebration across generations.
Our experts can help! Connect with more experts here: www.expertfile.com
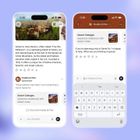
But there's a catch: You can’t just buy your way in ChatGPT will soon include “clearly labeled sponsored listings” at the bottom of AI-generated responses. And while the mock-ups don't appear all that sophisticated, it's important to focus on the bigger picture.
We're about to see a new wave of 'high-intent advertising' that combines the targeting sophistication of social media with the purchase-intent clarity of search advertising. More on that in a moment.
How Do ChatGPT Ads Work? Starting later this month, free users of the ChatGPT platform and those under 18 will begin receiving Ads at the bottom of their screens.
First, they will see ChatGPT's answer to their question, which provides a comprehensive, relevant response that builds trust.
Then they will see an ad for a sponsored product/service below. An ad that suddenly doesn't feel like a blunt interruption. It feels like a natural next step.
This is premium placement. The user has already received value. They've been educated. And now there's a clear call to action (CTA) that's in context. Open AI has stated that their new Ads “support a broader effort to make powerful AI accessible to more people.” Translation: As they approach 1 billion weekly users across 171 countries using ChatGPT for free, OpenAI needs to offset its astronomical burn rate with ads. Makes sense.
This New Era of Conversational Ads Will be Complicated But there's a structural difference with these new ads. OpenAI has stated that ads will only appear when they're relevant to that exact conversation.
This means you can't just buy your way into ChatGPT Ads. In fact, with ChatGPT you are being selected because you're the right answer the user needs at that time. Put another way: When ChatGPT evaluates which sponsored products to show, it will favor brands with demonstrated authority on the topic.
So unlike traditional paid search, where a higher bid gets you ranked in sponsored results, ChatGPT Ads will reward the brands whose content has already been recognized as authoritative by the AI model.
Brands with strong organic visibility, topical expertise, and content that aligns with user intent will have a distinct competitive advantage from day one. Brands without that foundation will be paying premium rates to compete with established authorities. How ChatGPT's Ad Strategy is Set to Change Digital Marketing For years, CMOs have treated organic search and paid search as separate budget lines, often managed by different teams. I saw this firsthand, as I helped my client DoubleClick launch it’s first Ad Exchange network in the US market. Programmatic exchanges brought a new efficiency to digital ad buying. It was a very groovy time.
This feels very different. Why? Because, the conventional wisdom has always been that paid search and ads drive immediate results while organic search plays the long game. In 2026, that strategy isn’t completely obsolete.
But that type of thinking is about to get a lot more expensive for clients if they don't start to appreciate quality "organic" content and its ability to improve their paid advertising ROI. Now organic and paid need to get along, to get ahead. ChatGPT Ads Are Looking for Topical Authority that Experts Can Demonstrate When ChatGPT evaluates which sponsored products to show, it will favor brands with demonstrated authority on the topic. Brands won't simply be able to "buy" visibility.
OpenAI in its announcements, has been explicit: ads must be relevant to the conversation. Relevance is determined by topical alignment, not budget. A brand spending millions on generic bidding will lose to a smaller competitor whose product is more precisely aligned with what the user actually asked.
The ads aren't live yet. But the infrastructure supporting them is. Open AI, Google and many of the other generative search platforms are building very sophisticated systems that track topical authority and content quality signals. They're already reshaping how organic search, AI recommendations, and paid advertising work together.
Topical Relevance + Expert Authority is the Path to Visibility in Search Investing in well-developed thought leadership programs generates compound returns. You get the organic search results plus an improvement in your paid search metrics in Generative AI search platforms. When done right, you build authority for AI citations, which then positions you better for ChatGPT ads.
Remember, your organic traffic gains are built on authoritative content. They're built on being the answer that search engines and AI systems select. And once you've built that authority, it works everywhere—traditional search, AI Overviews, ChatGPT, and soon… ChatGPT ads.
What To Do Before AI Ad Networks Start to Scale The early advantage will go to brands that invest in quality content right now. Organizations that invest in expert-authored, intent-aligned content over the next six months will have more AI citation visibility from Google Overviews and similar LLM's like ChatGPT. That means more trust signals, making paid ads more effective when they run.
Content that is aligned with user intent: Answers a specific question. Not tangentially, not after 2,000 words of context. The answer appears in the opening paragraph, structured for AI extraction.
Includes expert perspective. Generic information that could come from anywhere doesn't differentiate you. Expert insight, original research, or proprietary frameworks do.
Demonstrates topical authority. A single authoritative article matters less than a cluster of related content that shows comprehensive expertise on a topic.
Is structured for scanning. Clear headings (H2, H3), bullet points, tables, Q&A blocks. This structure helps both human readers and AI systems parse meaning.
Remember, the brands that get the most value out of ChatGPT Ads will be the ones that built intent-aligned content years before the ads launched. They'll have topical clusters, expert perspectives, and the authority signals that make them the natural choice for sponsorship. Questions CMO’s Should Be Asking their Teams Now to Prepare for ChatGPT Ads Q. Can I pre-purchase Chat GPT Ads? As of today, there are currently no ads in ChatGPT. Open AI has announced that they will begin internal testing ads in ChatGPT later this month for Free users in the US market.
Q. Do Ads influence the answers ChatGPT gives you? What about privacy? Open AI in their release states that answers are optimized based on what's most helpful to you. Ads are always separated and clearly labeled from Answers. They also state that they keep your conversations private from advertisers and will never sell your data to advertisers.
Q. How do we audit our site content to ensure we're aligned with user intent? For your top 20-30 decision-stage queries (the ones that drive revenue), here's a quick test. Does the content directly answer the question in the opening paragraph? Are you including question-and-answer formats in your content? If you're burying the answer in a 3,000-word article full of tangents, you're losing visibility in organic search, and you're already failing in ChatGPT's environment. Restructure.
Q. How do we prepare for ChatGPT Advertising Opportunities? Build topical authority through content clusters. Don't publish isolated blog posts. Organize your content around core topics your audience cares about. Create a long-form hub article that comprehensively covers the topic, then develop additional linked articles that dive into sub-topics and questions. Link them together. This structure helps AI systems over time, recognize your brand as authoritative on that topic, which improves both organic rankings and AI citation rates.
Q. Can we still get traction with content that is not authored by experts? Generic AI-written content won't differentiate you. Get expert voices into your content. Feature your subject-matter experts, partner with practitioners, and customers to contribute original insights, case studies, or frameworks. AI systems can detect authenticity, and original expert perspectives is now a ranking signal. This is especially critical as you prepare for ChatGPT ads. OpenAI has prioritized conversations that cite authoritative sources.
Q. How does content need to be structured for citations? Implement proper schema markup and structured data. AI systems extract information by parsing content structure. If your pages include proper schema markup (FAQPage, HowTo, Review, Product schema), you're making it easier for AI to pull your content into answers. This increases citation rates, which builds authority before ChatGPT ads scale.
Q. How do we allocate our organic and paid programs? Own the organic + paid intersection. For your highest-intent topics, if you have a budget, invest in both organic visibility and paid campaigns. Run ads targeting the same keywords where you rank organically. This takes up more real estate on the results page and signals authority. It also gives you direct feedback on keyword performance, messaging, and landing page effectiveness—data that informs your organic content strategy and drives more citations - a virtuous cycle.
Q. What types of creative will work best in these new Ad products? Until they roll out, it's unwise to make too many predictions. The safe bet here is to prepare your team for conversational advertising. ChatGPT ads won't reward traditional ad copy. They'll reward clarity, specificity, and direct value messaging. If you're used to brand-heavy, aspirational creative, this will feel foreign. Start testing conversationally-appropriate messaging now. Short, clear, problem-focused. Test on existing paid channels and refine before ChatGPT ads launch.
Our Prediction When ChatGPT ads fully launch and scale, many brands that have invested in organic visibility and content quality will start to pull away from the pack.
Remember…The brands that win won't be the ones with the biggest ad budgets. They'll be the ones whose content has already proven they're the right answer. They'll be the ones users already trust, already cite, and already know.
The ads are coming. Are you ready?





