Experts Matter. Find Yours.
Connect for media, speaking, professional opportunities & more.

Kelley School expert explains changing market conditions leading up to GM announcement
General Motors on Nov. 26 announced plans to close five manufacturing sites and consolidate production in North America and eliminate an estimated 14,000 white collar and blue-collar jobs. Rodney Parker, associate professor of operations management at Indiana University’s Kelley School of Business, said the announcement reflects several new realities for GM. “First, it reflects the ongoing shift of consumers preferences from cars to SUVS and pickups. The announcement to discontinue several cars models and focus more on trucks mirrors Ford’s announcement in April 2018 to drop all car models other than the Mustang and Focus to concentrate on trucks. SUVs and pickups are more profitable and they are what consumers want. “Consequently, GM has numerous plants which are under-utilized but still incur substantial fixed costs, resulting in losses. The plant closures are necessary for the whole company to remain profitable and competitive with rivals which are making similar moves. “Second, despite 2017 being a very good year for GM (record operating profit, sold over 10 million vehicles), sales in China can be credited for much of that success. The recent growth in the Chinese vehicle market has benefitted GM greatly and compensates for slower growth in the US domestic market. But the sales in China will necessarily be serviced by plants in China or nearby, rather than plants in the US. Also, the shift in production to more SUVs and pickups in the US plants caters to domestic tastes, not those in China. “Third, the substantial savings accrued from these closures will be necessary for future investments in autonomous vehicles (AVs) and electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrids. In 2016, GM wisely bought Cruise Automation, an AV startup in San Francisco, and has leapfrogged a number of auto rivals in this critical area. However, further development in AVs will require considerable investment by GM in order to keep pace with Google’s Waymo unit, with the possibility of launching their own ride-sharing service in the future. “Predictions for the automobile industry frequently suggest a shift from exclusively selling vehicles to also ‘selling miles,’ where the manufacturers are providing transportation services, through a combination of per usage fee or subscription. The economic argument for the usage of AVs in ride-sharing services is compelling and GM wants a part of this. At least part of the current plant closures are being done with an eye to the future and the big down payment GM needs to make in AVs.” Parker, who also is the Fettig/Whirlpool Faculty Fellow at Kelley, can be reached at 812-855-3329 or rodp@indiana.edu.

Why Some Mannequins Are Turning Blue, Taking a Dive and Putting on Weight
Baylor University fashion expert and author explains new twists in 'silent selling' -- and why frustrated customers may be relieved Women have long griped about pencil-thin mannequins in clothing displays, saying they bear little resemblance to real women’s bodies and make shopping frustrating and depressing. But the criticism is beginning to make inroads, and some members of the apparel industry are introducing changes to stop idealizing thin bodies and make mannequins more inclusive — among them creating mannequins with curvier shapes, modeling the figures after disabled people and, in a very different approach, fashioning forms that are totally unrealistic, says Baylor University researcher Lorynn Divita, Ph.D., co-author of the textbook "Fashion Forecasting” and associate professor of apparel merchandising in Baylor’s Robbins College of Health and Human Sciences. And more change may be in the works, prompted by research. A 2017 study published in the Journal of Eating Disorders found that 100 percent of the female mannequins studied in two large English cities represented an underweight body size — one that would be “medically unhealthy.” (Note: While female mannequins look scrawny, many of their male counterparts are brawny. Only 8 percent of male mannequins represented an underweight body size — although many appeared “unrealistically muscular,” researchers said.) Divita, who conducts research on the apparel industry, tracks trends and makes fashion predictions, offers some observations in this Q&A: Q: If mannequins are supposed to be a “silent seller” and a strong method for attracting customers, why are they so skinny that it is discouraging to women who are average or bigger? Why can’t their makers pack a few extra plastic pounds on them? A: For one thing, mannequins are expensive. The material for one that’s larger is going to cost more, the same way it is for plus-size garments, because you use more material. Typical department store mannequins can cost on average $500 to $900, and it can cost $150 just to repair a joint on a broken mannequin. In New York, where the retail industry is widely unionized, in some stores the sales associates are not allowed to touch the store mannequins. That responsibility is solely for visual merchandisers as a means of protecting the store’s investment. Another reason smaller mannequins have been appealing to retailers is that smaller dimensions make it easier to put on and remove clothing. Q: Wouldn’t it be worth the investment to make them bigger to showcase more realistic or inclusive figures and attract those customers? A: I recently visited the corporate offices of plus-size design company ELOQUII in New York, and their creative director, Jodi Arnold (B.S.H.E. ’88), shared with me that 65 percent of U.S. women are over size 14. Yet they represent only 17 percent of apparel spending. It’s hard to determine cause and effect: are they not spending on apparel because a wide variety of options aren’t available? Or is it that a wide variety of options are not available because this market does not spend on apparel? ELOQUII is betting on the former. In addition to their online store, they’ve recently begun opening brick-and-mortar storefronts which, unlike their website, feature merchandise on mannequins. Hopefully as the plus-sized apparel market continues to grow, the increased demand for plus-sized mannequins will result in wider representation of mannequin body types overall. Q: If most mannequins don’t reflect the majority of women’s physiques, where does the inspiration come for their sizes and shapes? A: Many mannequins can be sculpted using the measurements of live models or even have their proportions based on a celebrity who has a widely admired figure. Just like there is no standard apparel sizing system for women, there is no standard sizing system for display mannequins. Q: Besides beginning to be a bit more realistic in size, how are mannequins evolving? A: We are used to traditionally seeing mannequins in static poses like standing or sitting. With the rise in popularity of activewear, stores are devoting more floor space to this merchandise category, and it only makes sense to put those mannequins in dynamic positions like doing yoga poses or running. Another great example of dynamic poses can be found in swimwear: there are some great displays of mannequins diving. The impact of dynamic poses such as these are heightened when mannequins are displayed in groups of five or seven. Dynamic poses are currently being taken to the next level by actually suspending mannequins from the ceiling, so who knows how far this trend can go? One way to address representation is to go in the opposite direction and make a mannequin that is totally unrealistic. The last time I was shopping, I saw an entire section merchandised with glossy light-blue mannequins. This is actually a very clever way of appealing to everyone by targeting no one. Another interesting thing is that new technology allows visual merchandisers to creatively alter a mannequin’s appearance without changing it permanently by printing vinyl stickers to affix to mannequins’ faces. Merchandisers can print out bold lips or dramatic eyelashes, affix them to the mannequin in the display and easily take them off when they are done, which gives visual merchandisers yet another way to attract our attention. ABOUT LORYNN DIVITA, Ph.D. Divita is the author of the textbook “Fashion Forecasting” (Fourth edition, Fairchild Books). Her publications have appeared in the Journal of the Textile Institute and Journal of Fashion Marketing and Management, both published in England; Clothing and Textiles Research Journal and Journal of Textile and Apparel Technology and Management. She is the United States editor for the Bloomsbury Fashion Business Case Studies project and is on the editorial board of the Journal of Fashion, Style and Popular Culture. Divita received her B.A. in French and B.S. in fashion merchandising from California State University Chico, her Master’s degree in apparel manufacturing management from University of Missouri, and her Ph.D. in textile products marketing from University of North Carolina at Greensboro.

How to Negotiate the Best Retail Price: Baylor Expert Shares 11 Tips
Confidence in retail negotiations can lead to confidence in salary talks as well, management expert says In today’s retail climate, where stores struggle to keep up with online competition and customers can compare prices with the ease of their smartphones, the price tag is just a starting point for negotiations, said a negotiation expert at Baylor University. “No longer do you need to pay sticker price for everything you buy. The customer is now empowered to have a say in pricing, and even hourly retail workers are often empowered to give price discounts when requested,” said Emily Hunter, Ph.D., associate professor of management in Baylor University’s Hankamer School of Business, and an expert in negotiation and conflict management. Hunter said negotiations – whether in a retail setting or in the workplace – require confidence. “Many people are hesitant to negotiate because they don’t know how or they are worried about the other person’s reaction (Will they think I’m greedy?),” she said. “But practice can increase your confidence in your ability to negotiate. Rejection is less common than you fear, and retail stores especially are often willing to work with you.” She offered the following tips to increase the chances of greater deals at the check-out counter. Be nice. First and foremost, always be kind and polite when asking for a discount in retail settings, Hunter said. You are much more likely to be successful if someone wants to help you out, as opposed to demanding a discount or raising your voice to puff up your sense of power. It’s not a power play. Instead, negotiating is a matter of give-and-take. Find defects. It is easier to negotiate an item if you can find something wrong with it. Most stores have a policy in place that allows cashiers and salespeople to offer a moderate discount (typically 10-15 percent), but when they offer it, be persistent and politely try to push them for more. “I’ve negotiated a rug because it was on the sales floor and had frayed edges, a metal cabinet with a dent in the back (Who will ever see that? It’s in the back!), and clothing with a slight stain,” Hunter said. “Point out the defect to the person you are negotiating with and ask for half off.” Look for mark-downs. If an item is marked down or “open-box,” then ask for further discounts, Hunter advised. Remember, the store already acknowledged that the item is worth less than original price and they are likely desperate to be rid of it quickly. “Borrow” a coupon during check-out. When making a purchase, Hunter said she is often asked the question: “Do you have a coupon?” Instead of saying no, she said it might save some money to consider another reply. “Whenever I’m asked this question at check-out, I reply, ‘No, do you have one I could use?’ This works more often than you might think and can result in sweet savings. No clipping required,” she said. Prepare yourself – quickly. When you see an item that could be a good opportunity to negotiate, Hunter said it’s best to prepare quickly with three steps. First, set a strong goal for yourself, usually in the form of a steep discount you will request. Second, set a “redline” price, the highest price you are willing to pay. Third, consider your best alternative – which might be purchasing the same item online for less – if negotiations fail. Find a BATNA. “In negotiation lingo, we call your best alternative your BATNA – Best Alternative to a Negotiated Agreement,” Hunter said. “In retail, it’s extremely important to shop around both at other stores and online to see if the same or a similar item is offered elsewhere for less. This can be your bargaining chip to ask for a discount.” She explained that most big-box stores now have a price-matching policy, but it’s worth trying to go beyond the price match and ask for an additional 10 percent discount, particularly if you agree to purchase at that moment. “Think about it from the store’s perspective,” she said. “They want to keep you from buying from major online retailers, so they might agree to a discount.” Ask for a higher discount than you’re seeking. Let’s say you’re seeking $200 off the price of a refrigerator. Hunter said it’s not wise to start your negotiation by asking for $200 off, because you are almost guaranteed to get less than that. “In negotiations, both sides expect some give-and-take, and the retailer is unlikely to accept your first offer,” she said. “Start by asking for $500 off the fridge and see what they say. Even better, back up your offer by pointing out a defect, a cheaper price online for the same product or evidence of a sale at the same store that just ended.” Pretend you own the business. Think from the seller’s perspective, Hunter advised. Consider what the seller wants from you, the customer. Besides the obvious answer of higher sales and profit, simply offering to write a review online could be very helpful, especially for small businesses. “I once got a great deal on a tool cabinet because I offered to write a positive review on the customer experience survey (you know, the one you get on your receipt that few people fill out?). The manager said that would be wonderful because his store performance is assessed partly based on those customer surveys and he really needed a good review that quarter,” Hunter said. Always negotiate furniture. Hunter said the markup on furniture is often extremely high, as much as 80 percent, and that makes furniture a target for negotiation. “I always negotiate when buying everything from mattresses to sofas to end tables,” she said. “Ask for big discounts at first, as you never know how desperate they are to rotate their stock. And try asking for steeper discounts if you buy multiple pieces, or buying a sofa set and getting the coffee table thrown in for free.” Choose your opponent wisely. When you choose to negotiate, make sure you’re dealing with the people who can make the decisions, Hunter said. Sometimes the clerks on the floor might not be the best option, so jump straight to the cashier or the manager to work with someone who has the authority to make a pricing decision. Remember the ultimate goal. Negotiation is not just about saving a few dollars, Hunter said. Instead, it’s about building negotiating skills. “Negotiating in retail settings can be a helpful practice to build your confidence to negotiate more important items such as salary and work projects,” she said. “While negotiating salary and other relationship-based issues at work differs quite a bit from the strategies described here, the first step is having the confidence to ask.” ABOUT EMILY HUNTER, PH.D. Emily Hunter, Ph.D., associate professor of management in Baylor University's Hankamer School of Business, teaches negotiation and conflict management. Her research on employee work-family issues, workday breaks and deviant behavior has appeared in academic journals such as Journal of Applied Psychology, Journal of Management and Journal of Organizational Behavior. She is also the co-author of "Organized Innovation: A Blueprint for Renewing America's Prosperity." ABOUT BAYLOR UNIVERSITY Baylor University is a private Christian University and a nationally ranked research institution. The University provides a vibrant campus community for more than 17,000 students by blending interdisciplinary research with an international reputation for educational excellence and a faculty commitment to teaching and scholarship. Chartered in 1845 by the Republic of Texas through the efforts of Baptist pioneers, Baylor is the oldest continually operating University in Texas. Located in Waco, Baylor welcomes students from all 50 states and more than 80 countries to study a broad range of degrees among its 12 nationally recognized academic divisions. ABOUT BAYLOR’S HANKAMER SCHOOL OF BUSINESS Baylor University’s Hankamer School of Business provides a rigorous academic experience, consisting of classroom and hands-on learning, guided by Christian commitment and a global perspective. Recognized nationally for several programs, including Entrepreneurship and Accounting, the school offers 24 undergraduate and 13 graduate areas of study. Visit www.baylor.edu/businessand follow on Twitter at twitter.com/Baylor_Business.

One Tweak That Can (Instantly) Add Significantly To The Value Of Your Business
If you’re trying to figure out what your business might be worth, it’s helpful to consider what acquirers are paying for companies like yours these days. A little internet research will probably reveal that a business trades for a multiple of your pre-tax profit, which is Sellers Discretionary Earnings (SDE) for a small business and Earnings Before Interest Taxes, Depreciation and Amortization (EBITDA) for a slightly larger business. Ian Fitzpatrick is a Chartered Professional Accountant and a Chartered Business Valuator. He is an expert in advising business owners and entrepreneurs on all aspects of corporate sales, mergers, acquisitions, litigation, succession and ownership issues. In a recent piece, Ian highlights how business owners can take simple steps to add significant value to their enterprises. To learn more, simply click on the short article attached at the bottom. To contact Ian directly, simply click on his icon to arrange an appointment regarding this topic. Source:

Forecasting sales using financial stock market data
Firms use many kinds of data for forecasting future sales—one of the key activities in the management of a business—and combine various methods in order to utilize different types of information. A recent study by Nikolay Osadchiy, assistant professor of information systems and operations management; Vishal Gaur (Cornell); and Sridhar Seshadri (UT Austin) focuses on financial stock market data in developing a new methodology for firm-level sales forecasting, testing it against standard benchmarks such as forecasts from equity analysts and time-series methods. Applying their method to the forecast of total annual sales for US public retail firms, the researchers find their market-based approach achieves an average 15 percent reduction in forecasting error compared with more typical forecasting methods. Their model, they write, can also be applied to hedging operational risk with financial instruments. Source:

Luxury retailers, customer experience, and brand desire
Consumers often complain that sales staff at luxury retailers ignore or reject average customers. Employees in the industry confirm that sales staff at luxury retailers do sometimes size up customers, choosing who to help and who to avoid based on what they wear. Conventional wisdom would suggest that the rejected consumer would choose not to buy the specific brand. Morgan Ward, assistant professor of marketing, and coauthor Darren W. Dahl (U of British Columbia) challenge this idea “by exploring how negative customer service experiences can, in some instances, facilitate more positive attitudes and customers’ desire for the brand.” The pair tested their theory by providing study participants with a variety of shopping scenarios involving being rejected versus receiving a neutral response from the salesperson while in a luxury retailer. Ward and Dahl discover that shoppers who “relate their self-concept to an aspirational brand” become more motivated to buy that luxury brand after a salesperson’s rejection, in order to be accepted by what they perceive as the in-crowd. Source:

Supply network structure and systemic risk
Demand uncertainty can present a serious challenge for any business, especially when it comes to managerial decisions on inventory. But when an economic downturn happens, the challenge becomes systemic. According to research by Nikolay Osadchiy, assistant professor of information systems & operations management, and coauthors Vishal Gaur (Cornell U) and Sridhar Seshadri (Indian School of Business), systemic risk is more greatly felt depending on where a company sits in the supply chain. The trio discovered that while an economic downturn presented a serious hurdle for retailers, wholesalers, and manufacturers alike, manufacturers were more prone to systemic risk given their placement upstream in the supply chain. Manufacturers had “a more dispersed customer base,” which the authors noted was more closely “associated with higher systematic risk.” Manufacturers also experienced greater systemic risk due to the effect of aggregation of orders over time. They wrote, “A market shock in one period may affect sales over several periods due to lead times and time lags in managerial decision making.” Source:
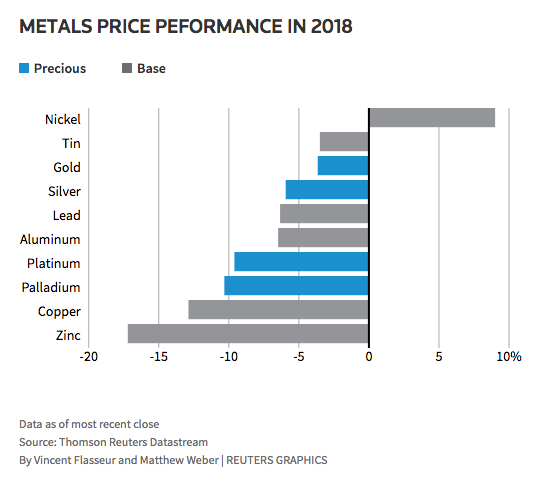
With the shine coming back on nickel – what will it mean for Ontario’s local and wider economies.
It’s boom or bust in the nickel business. From cycles, to slumps to super-cycles and even the most recent decade-long crash, it appears the time for nickel to rebound is near. The last big boom at the turn of the 21st Century saw nickel soar above 20 dollars per pound. It led to multi-billion dollar takeovers of smaller mining companies by industry giants and saw local economies flourish as bonuses skyrocketed, overtime was uncapped and investments in service, supply, innovation and industry support were elevated almost exponentially. Today, with analysts projecting the price of nickel to at least double over the next four years, what can local and provincial economies expect? After a 10-year slump can we expect the same rush to invest and spend? Will companies be more cautious and what will it mean for investors, the markets and businesses. There are a lot of questions and speculation out there about just how big of a splash there will be if nickel finally makes its comeback. And that’s where the experts from Freelandt Caldwell Reilly LLP can help. Ian Fitzpatrick is a Chartered Professional Accountant and a Chartered Business Valuator. He is an expert in advising business owners and entrepreneurs on all aspects of corporate sales, mergers, acquisitions, litigation, succession and ownership issues. To contact Ian directly, simply click on his icon to arrange an appointment regarding this topic. Source:

Dell Regains Top Share in the Canadian PC Commercial Market
There’s good news today for Dell Canada. The computer company based in Round Rock, Texas posted the strongest year-on-year growth out of all the major companies in Canada - growing 11.9% and buoyed by strong performances in the public sector segments. These numbers are impressive as shipments of traditional PCs in the first quarter of 2018 totalled 1.25 million units into the Canadian Market. Though the worldwide numbers show a flat (0.0%) year-on-year growth in the first quarter, the expectations exceeded the earlier forecast of a 1.5% decline in PC sales. The Canadian market was a bright light growing 4.2% annually. But it wasn’t all good news in Canada, out of the top five leading companies that also include HP, Dell, Lenovo, Acer and Apple. It was Apple that lost its shine finishing last with a year-on-year decline in shipments of 5.8%. So, what does this mean for the industry? Are PC’s coming back against the popular tide of tablets and other competing units? What is Dell doing right to lead the way? And what’s next for developers as they look to the next generation of products. There’s a lot to more to this topic – and that’s where an expert from the International Data Corporation (IDC) can help. Tim Brunt is the Program Manager for IDC's Canadian Quarterly PC Tracker program. He is an expert in analyzing current market trends, business planning, business and consumer buyer behavior. Tim is available to speak with media, simply click on his icon to arrange an interview. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/canadian-traditional-pc-market-grew-42-yoy-q1-2018-tim-brunt/

Movies like “Marshall” that are built around actors of color (Chadwick Boseman plays the iconic attorney) and have appeal to consumers of color historically see a significant surge in ticket sales in weeks five through eight – if producers are willing to keep them in theaters that long and allow for word-of-mouth advertising to build, said Tyrha Lindsey-Warren, Ph.D., clinical assistant professor of marketing in Baylor’s Hankamer School of Business. She studies consumer behavior, multicultural media, movies and entertainment. “I believe that Hollywood often pulls movies starring women and actors of color out of the theaters way too soon and before word-of-mouth has time to fully spread,” Lindsey-Warren said. “In my opinion, and according to our studies, Hollywood is leaving a great deal of money on the table.” Movies built around actors of color typically make money – in many cases as much or more than five times the budget, she said. For example, the 2017 comedy “Girls Trip,” which was built around four African-American female leads, was made for $19 million and has grossed more than $100 million at the box office. A challenge, Lindsey-Warren said, is that Hollywood expects to make its money back in the opening weekend. That strategy often doesn’t translate well to consumers of color. She cited a Nielsen study that showed African-Americans make an average 6.3 trips every year to see movies, and they tend to strongly support movies where there are characters like themselves and to whom they can relate. But they don’t rush to theaters for premier weekends. “Historically, African-American consumers have not been such early adopters of seeing movies on opening weekend and have typically waited to hear from trusted sources, by way of word-of-mouth, if the movie is worth seeing,” she said. “I call this behavior giving word-of-mouth time to spread. These are insights that Hollywood has not fully embraced regarding consumers of color and for movies built around actors of color.” Source:





